Facebook founder Mark Zuckerberg’s visage loomed large over the European parliament this week, both literally and figuratively, as global privacy regulators gathered in Brussels to interrogate the human impacts of technologies that derive their power and persuasiveness from our data.
The eponymous social network has been at the center of a privacy storm this year. And every fresh Facebook content concern — be it about discrimination or hate speech or cultural insensitivity — adds to a damaging flood.
The overarching discussion topic at the privacy and data protection confab, both in the public sessions and behind closed doors, was ethics: How to ensure engineers, technologists and companies operate with a sense of civic duty and build products that serve the good of humanity.
So, in other words, how to ensure people’s information is used ethically — not just in compliance with the law. Fundamental rights are increasingly seen by European regulators as a floor not the ceiling. Ethics are needed to fill the gaps where new uses of data keep pushing in.
As the EU’s data protection supervisor, Giovanni Buttarelli, told delegates at the start of the public portion of the International Conference of Data Protection and Privacy Commissioners: “Not everything that is legally compliant and technically feasible is morally sustainable.”
As if on cue Zuckerberg kicked off a pre-recorded video message to the conference with another apology. Albeit this was only for not being there to give an address in person. Which is not the kind of regret many in the room are now looking for, as fresh data breaches and privacy incursions keep being stacked on top of Facebook’s Cambridge Analytica data misuse scandal like an unpalatable layer cake that never stops being baked.
Evidence of a radical shift of mindset is what champions of civic tech are looking for — from Facebook in particular and adtech in general.
But there was no sign of that in Zuckerberg’s potted spiel. Rather he displayed the kind of masterfully slick PR manoeuvering that’s associated with politicians on the campaign trail. It’s the natural patter for certain big tech CEOs too, these days, in a sign of our sociotechnical political times.
(See also: Facebook hiring ex-UK deputy PM, Nick Clegg, to further expand its contacts database of European lawmakers.)
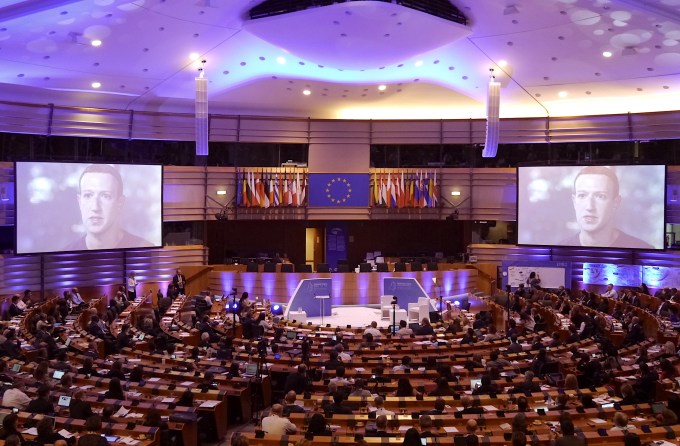

And so the Facebook founder seized on the conference’s discussion topic of big data ethics and tried to zoom right back out again. Backing away from talk of tangible harms and damaging platform defaults — aka the actual conversational substance of the conference (from talk of how dating apps are impacting how much sex people have and with whom they’re doing it; to shiny new biometric identity systems that have rebooted discriminatory caste systems) — to push the idea of a need to “strike a balance between speech, security, privacy and safety”.
This was Facebook trying reframe the idea of digital ethics — to make it so very big-picture-y that it could embrace his people-tracking ad-funded business model as a fuzzily wide public good, with a sort of ‘oh go on then’ shrug.
“Every day people around the world use our services to speak up for things they believe in. More than 80 million small businesses use our services, supporting millions of jobs and creating a lot of opportunity,” said Zuckerberg, arguing for a ‘both sides’ view of digital ethics. “We believe we have an ethical responsibility to support these positive uses too.”
Indeed, he went further, saying Facebook believes it has an “ethical obligation to protect good uses of technology”.
And from that self-serving perspective almost anything becomes possible — as if Facebook is arguing that breaking data protection law might really be the ‘ethical’ thing to do. (Or, as the existentialists might put it: ‘If god is dead, then everything is permitted’.)
It’s an argument that radically elides some very bad things, though. And glosses over problems that are systemic to Facebook’s ad platform.
A little later, Google’s CEO Sundar Pichai also dropped into the conference in video form, bringing much the same message.
“The conversation about ethics is important. And we are happy to be a part of it,” he began, before an instant hard pivot into referencing Google’s founding mission of “organizing the world’s information — for everyone” (emphasis his), before segwaying — via “knowledge is empowering” — to asserting that “a society with more information is better off than one with less”.
Is having access to more information of unknown and dubious or even malicious provenance better than having access to some verified information? Google seems to think so.
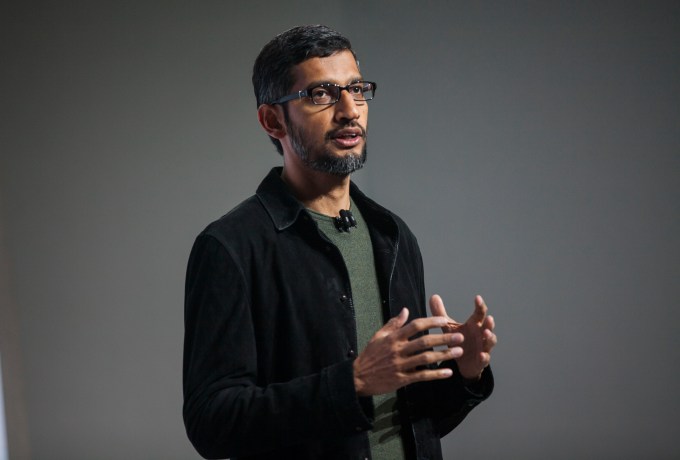

SAN FRANCISCO, CA – OCTOBER 04: Pichai Sundararajan, known as Sundar Pichai, CEO of Google Inc. speaks during an event to introduce Google Pixel phone and other Google products on October 4, 2016 in San Francisco, California. The Google Pixel is intended to challenge the Apple iPhone in the premium smartphone category. (Photo by Ramin Talaie/Getty Images)
The pre-recorded Pichai didn’t have to concern himself with all the mental ellipses bubbling up in the thoughts of the privacy and rights experts in the room.
“Today that mission still applies to everything we do at Google,” his digital image droned on, without mentioning what Google is thinking of doing in China. “It’s clear that technology can be a positive force in our lives. It has the potential to give us back time and extend opportunity to people all over the world.
“But it’s equally clear that we need to be responsible in how we use technology. We want to make sound choices and build products that benefit society that’s why earlier this year we worked with our employees to develop a set of AI principles that clearly state what types of technology applications we will pursue.”
Of course it sounds fine. Yet Pichai made no mention of the staff who’ve actually left Google because of ethical misgivings. Nor the employees still there and still protesting its ‘ethical’ choices.
It’s not almost as if the Internet’s adtech duopoly is singing from the same ‘ads for greater good trumping the bad’ hymn sheet; the Internet’s adtech’s duopoly is doing exactly that.
The ‘we’re not perfect and have lots more to learn’ line that also came from both CEOs seems mostly intended to manage regulatory expectation vis-a-vis data protection — and indeed on the wider ethics front.
They’re not promising to do no harm. Nor to always protect people’s data. They’re literally saying they can’t promise that. Ouch.
Meanwhile, another common FaceGoog message — an intent to introduce ‘more granular user controls’ — just means they’re piling even more responsibility onto individuals to proactively check (and keep checking) that their information is not being horribly abused.
This is a burden neither company can speak to in any other fashion. Because the solution is that their platforms not hoard people’s data in the first place.
The other ginormous elephant in the room is big tech’s massive size; which is itself skewing the market and far more besides.
Neither Zuckerberg nor Pichai directly addressed the notion of overly powerful platforms themselves causing structural societal harms, such as by eroding the civically minded institutions that are essential to defend free societies and indeed uphold the rule of law.
Of course it’s an awkward conversation topic for tech giants if vital institutions and societal norms are being undermined because of your cut-throat profiteering on the unregulated cyber seas.
A great tech fix to avoid answering awkward questions is to send a video message in your CEO’s stead. And/or a few minions. Facebook VP and chief privacy officer, Erin Egan, and Google’s SVP of global affairs Kent Walker, were duly dispatched and gave speeches in person.
They also had a handful of audience questions put to them by an on stage moderator. So it fell to Walker, not Pichai, to speak to Google’s contradictory involvement in China in light of its foundational claim to be a champion of the free flow of information.
“We absolutely believe in the maximum amount of information available to people around the world,” Walker said on that topic, after being allowed to intone on Google’s goodness for almost half an hour. “We have said that we are exploring the possibility of ways of engaging in China to see if there are ways to follow that mission while complying with laws in China.
“That’s an exploratory project — and we are not in a position at this point to have an answer to the question yet. But we continue to work.”
Egan, meanwhile, batted away her trio of audience concerns — about Facebook’s lack of privacy by design/default; and how the company could ever address ethical concerns without dramatically changing its business model — by saying it has a new privacy and data use team sitting horizontally across the business, as well as a data protection officer (an oversight role mandated by the EU’s GDPR; into which Facebook plugged its former global deputy chief privacy officer, Stephen Deadman, earlier this year).
She also said the company continues to invest in AI for content moderation purposes. So, essentially, more trust us. And trust our tech.
She also replied in the affirmative when asked whether Facebook will “unequivocally” support a strong federal privacy law in the US — with protections “equivalent” to those in Europe’s data protection framework.
But of course Zuckerberg has said much the same thing before — while simultaneously advocating for weaker privacy standards domestically. So who now really wants to take Facebook at its word on that? Or indeed on anything of human substance.
Not the EU parliament, for one. MEPs sitting in the parliament’s other building, in Strasbourg, this week adopted a resolution calling for Facebook to agree to an external audit by regional oversight bodies.
But of course Facebook prefers to run its own audit. And in a response statement the company claims it’s “working relentlessly to ensure the transparency, safety and security” of people who use its service (so bad luck if you’re one of those non-users it also tracks then). Which is a very long-winded way of saying ‘no, we’re not going to voluntarily let the inspectors in’.
Facebook’s problem now is that trust, once burnt, takes years and mountains’ worth of effort to restore.
This is the flip side of ‘move fast and break things’. (Indeed, one of the conference panels was entitled ‘move fast and fix things’.) It’s also the hard-to-shift legacy of an unapologetically blind ~decade-long dash for growth regardless of societal cost.
Given the, it looks unlikely that Zuckerberg’s attempt to paint a portrait of digital ethics in his company’s image will do much to restore trust in Facebook.
Not so long as the platform retains the power to cause damage at scale.
It was left to everyone else at the conference to discuss the hollowing out of democratic institutions, societal norms, humans interactions and so on — as a consequence of data (and market capital) being concentrated in the hands of the ridiculously powerful few.
“Today we face the gravest threat to our democracy, to our individual liberty in Europe since the war and the United States perhaps since the civil war,” said Barry Lynn, a former journalist and senior fellow at the Google-backed New America Foundation think tank in Washington, D.C., where he had directed the Open Markets Program — until it was shut down after he wrote critically about, er, Google.
“This threat is the consolidation of power — mainly by Google, Facebook and Amazon — over how we speak to one another, over how we do business with one another.”
Meanwhile the original architect of the World Wide Web, Tim Berners-Lee, who has been warning about the crushing impact of platform power for years now is working on trying to decentralize the net’s data hoarders via new technologies intended to give users greater agency over their data.
On the democratic damage front, Lynn pointed to how news media is being hobbled by an adtech duopoly now sucking hundreds of billion of ad dollars out of the market annually — by renting out what he dubbed their “manipulation machines”.
Not only do they sell access to these ad targeting tools to mainstream advertisers — to sell the usual products, like soap and diapers — they’re also, he pointed out, taking dollars from “autocrats and would be autocrats and other social disruptors to spread propaganda and fake news to a variety of ends, none of them good”.
The platforms’ unhealthy market power is the result of a theft of people’s attention, argued Lynn. “We cannot have democracy if we don’t have a free and robustly funded press,” he warned.
His solution to the society-deforming might of platform power? Not a newfangled decentralization tech but something much older: Market restructuring via competition law.
“The basic problem is how we structure or how we have failed to structure markets in the last generation. How we have licensed or failed to license monopoly corporations to behave.
“In this case what we see here is this great mass of data. The problem is the combination of this great mass of data with monopoly power in the form of control over essential pathways to the market combined with a license to discriminate in the pricing and terms of service. That is the problem.”
“The result is to centralize,” he continued. “To pick and choose winners and losers. In other words the power to reward those who heed the will of the master, and to punish those who defy or question the master — in the hands of Google, Facebook and Amazon… That is destroying the rule of law in our society and is replacing rule of law with rule by power.”
For an example of an entity that’s currently being punished by Facebook’s grip on the social digital sphere you need look no further than Snapchat.
Also on the stage in person: Apple’s CEO Tim Cook, who didn’t mince his words either — attacking what he dubbed a “data industrial complex” which he said is “weaponizing” people’s person data against them for private profit.
The adtech modeus operandi sums to “surveillance”, Cook asserted.
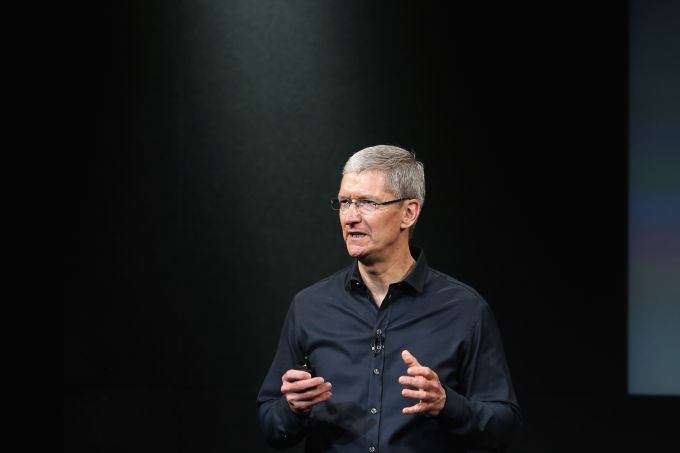

Cook called this a “crisis”, painting a picture of technologies being applied in an ethics-free vacuum to “magnify our worst human tendencies… deepen divisions, incite violence and even undermine our shared sense of what is true and what is false” — by “taking advantage of user trust”.
“This crisis is real… And those of us who believe in technology’s potential for good must not shrink from this moment,” he warned, telling the assembled regulators that Apple is aligned with their civic mission.
Of course Cook’s position also aligns with Apple’s hardware-dominated business model — in which the company makes most of its money by selling premium priced, robustly encrypted devices, rather than monopolizing people’s attention to sell their eyeballs to advertisers.
The growing public and political alarm over how big data platforms stoke addiction and exploit people’s trust and information — and the idea that an overarching framework of not just laws but digital ethics might be needed to control this stuff — dovetails neatly with the alternative track that Apple has been pounding for years.
So for Cupertino it’s easy to argue that the ‘collect it all’ approach of data-hungry platforms is both lazy thinking and irresponsible engineering, as Cook did this week.
“For artificial intelligence to be truly smart it must respect human values — including privacy,” he said. “If we get this wrong, the dangers are profound. We can achieve both great artificial intelligence and great privacy standards. It is not only a possibility — it is a responsibility.”
Yet Apple is not only a hardware business. In recent years the company has been expanding and growing its services business. It even involves itself in (a degree of) digital advertising. And it does business in China.
It is, after all, still a for-profit business — not a human rights regulator. So we shouldn’t be looking to Apple to spec out a digital ethical framework for us, either.
No profit making entity should be used as the model for where the ethical line should lie.
Apple sets a far higher standard than other tech giants, certainly, even as its grip on the market is far more partial because it doesn’t give its stuff away for free. But it’s hardly perfect where privacy is concerned.
One inconvenient example for Apple is that it takes money from Google to make the company’s search engine the default for iOS users — even as it offers iOS users a choice of alternatives (if they go looking to switch) which includes pro-privacy search engine DuckDuckGo.
DDG is a veritable minnow vs Google, and Apple builds products for the consumer mainstream, so it is supporting privacy by putting a niche search engine alongside a behemoth like Google — as one of just four choices it offers.
But defaults are hugely powerful. So Google search being the iOS default means most of Apple’s mobile users will have their queries fed straight into Google’s surveillance database, even as Apple works hard to keep its own servers clear of user data by not collecting their stuff in the first place.
There is a contradiction there. So there is a risk for Apple in amping up its rhetoric against a “data industrial complex” — and making its naturally pro-privacy preference sound like a conviction principle — because it invites people to dial up critical lenses and point out where its defence of personal data against manipulation and exploitation does not live up to its own rhetoric.
One thing is clear: In the current data-based ecosystem all players are conflicted and compromised.
Though only a handful of tech giants have built unchallengeably massive tracking empires via the systematic exploitation of other people’s data.
And as the apparatus of their power gets exposed, these attention-hogging adtech giants are making a dumb show of papering over the myriad ways their platforms pound on people and societies — offering paper-thin promises to ‘do better next time — when ‘better’ is not even close to being enough.
Call for collective action
Increasingly powerful data-mining technologies must be sensitive to human rights and human impacts, that much is crystal clear. Nor is it enough to be reactive to problems after or even at the moment they arise. No engineer or system designer should feel it’s their job to manipulate and trick their fellow humans.
Dark pattern designs should be repurposed into a guidebook of what not to do and how not to transact online. (If you want a mission statement for thinking about this it really is simple: Just don’t be a dick.)
Sociotechnical Internet technologies must always be designed with people and societies in mind — a key point that was hammered home in a keynote by Berners-Lee, the inventor of the World Wide Web, and the tech guy now trying to defang the Internet’s occupying corporate forces via decentralization.
“As we’re designing the system, we’re designing society,” he told the conference. “Ethical rules that we choose to put in that design [impact society]… Nothing is self evident. Everything has to be put out there as something that we think we will be a good idea as a component of our society.”
The penny looks to be dropping for privacy watchdogs in Europe. The idea that assessing fairness — not just legal compliance — must be a key component of their thinking, going forward, and so the direction of regulatory travel.
Watchdogs like the UK’s ICO — which just fined Facebook the maximum possible penalty for the Cambridge Analytica scandal — said so this week. “You have to do your homework as a company to think about fairness,” said Elizabeth Denham, when asked ‘who decides what’s fair’ in a data ethics context. “At the end of the day if you are working, providing services in Europe then the regulator’s going to have something to say about fairness — which we have in some cases.”
“Right now, we’re working with some Oxford academics on transparency and algorithmic decision making. We’re also working on our own tool as a regulator on how we are going to audit algorithms,” she added. “I think in Europe we’re leading the way — and I realize that’s not the legal requirement in the rest of the world but I believe that more and more companies are going to look to the high standard that is now in place with the GDPR.
“The answer to the question is ‘is this fair?’ It may be legal — but is this fair?”
So the short version is data controllers need to prepare themselves to consult widely — and examine their consciences closely.
Rising automation and AI makes ethical design choices even more imperative, as technologies become increasingly complex and intertwined, thanks to the massive amounts of data being captured, processed and used to model all sorts of human facets and functions.
The closed session of the conference produced a declaration on ethics and data in artificial intelligence — setting out a list of guiding principles to act as “core values to preserve human rights” in the developing AI era — which included concepts like fairness and responsible design.
Few would argue that a powerful AI-based technology such as facial recognition isn’t inherently in tension with a fundamental human right like privacy.
Nor that such powerful technologies aren’t at huge risk of being misused and abused to discriminate and/or suppress rights at vast and terrifying scale. (See, for example, China’s push to install a social credit system.)
Biometric ID systems might start out with claims of the very best intentions — only to shift function and impact later. The dangers to human rights of function creep on this front are very real indeed. And are already being felt in places like India — where the country’s Aadhaar biometric ID system has been accused of rebooting ancient prejudices by promoting a digital caste system, as the conference also heard.
The consensus from the event is it’s not only possible but vital to engineer ethics into system design from the start whenever you’re doing things with other people’s data. And that routes to market must be found that don’t require dispensing with a moral compass to get there.
The notion of data-processing platforms becoming information fiduciaries — i.e. having a legal duty of care towards their users, as a doctor or lawyer does — was floated several times during public discussions. Though such a step would likely require more legislation, not just adequately rigorous self examination.
In the meanwhile civic society must get to grips, and grapple proactively, with technologies like AI so that people and societies can come to collective agreement about a digital ethics framework. This is vital work to defend the things that matter to communities so that the anthropogenic platforms Berners-Lee referenced are shaped by collective human values, not the other way around.
It’s also essential that public debate about digital ethics does not get hijacked by corporate self interest.
Tech giants are not only inherently conflicted on the topic but — right across the board — they lack the internal diversity to offer a broad enough perspective.
People and civic society must teach them.
A vital closing contribution came from the French data watchdog’s Isabelle Falque-Pierrotin, who summed up discussions that had taken place behind closed doors as the community of global data protection commissioners met to plot next steps.
She explained that members had adopted a roadmap for the future of the conference to evolve beyond a mere talking shop and take on a more visible, open governance structure — to allow it to be a vehicle for collective, international decision-making on ethical standards, and so alight on and adopt common positions and principles that can push tech in a human direction.
The initial declaration document on ethics and AI is intended to be just the start, she said — warning that “if we can’t act we will not be able to collectively control our future”, and couching ethics as “no longer an option, it is an obligation”.
She also said it’s essential that regulators get with the program and enforce current privacy laws — to “pave the way towards a digital ethics” — echoing calls from many speakers at the event for regulators to get on with the job of enforcement.
This is vital work to defend values and rights against the overreach of the digital here and now.
“Without ethics, without an adequate enforcement of our values and rules our societal models are at risk,” Falque-Pierrotin also warned. “We must act… because if we fail, there won’t be any winners. Not the people, nor the companies. And certainly not human rights and democracy.”
If the conference had one short sharp message it was this: Society must wake up to technology — and fast.
“We’ve got a lot of work to do, and a lot of discussion — across the boundaries of individuals, companies and governments,” agreed Berners-Lee. “But very important work.
“We have to get commitments from companies to make their platforms constructive and we have to get commitments from governments to look at whenever they see that a new technology allows people to be taken advantage of, allows a new form of crime to get onto it by producing new forms of the law. And to make sure that the policies that they do are thought about in respect to every new technology as they come out.”
This work is also an opportunity for civic society to define and reaffirm what’s important. So it’s not only about mitigating risks.
But, equally, not doing the job is unthinkable — because there’s no putting the AI genii back in the bottle.

from Apple – TechCrunch https://ift.tt/2OTqNR3








 Again, the biggest barrier to this path is Spiegel. Combine totalitarian voting control with the
Again, the biggest barrier to this path is Spiegel. Combine totalitarian voting control with the  Increasingly, Apple must rely on its iOS software to compete for customers with Android headsets. But you know who’s great at making interesting software? Snapchat. You know who has a great relationship with the next generation of phone owners? Snapchat. And do you know whose CEO could probably smile earnestly beside Tim Cook announcing a brighter future for social media unlocked by two privacy-focused companies joining forces? Snapchat. Plus, think of all the fun Snapple jokes?
Increasingly, Apple must rely on its iOS software to compete for customers with Android headsets. But you know who’s great at making interesting software? Snapchat. You know who has a great relationship with the next generation of phone owners? Snapchat. And do you know whose CEO could probably smile earnestly beside Tim Cook announcing a brighter future for social media unlocked by two privacy-focused companies joining forces? Snapchat. Plus, think of all the fun Snapple jokes?