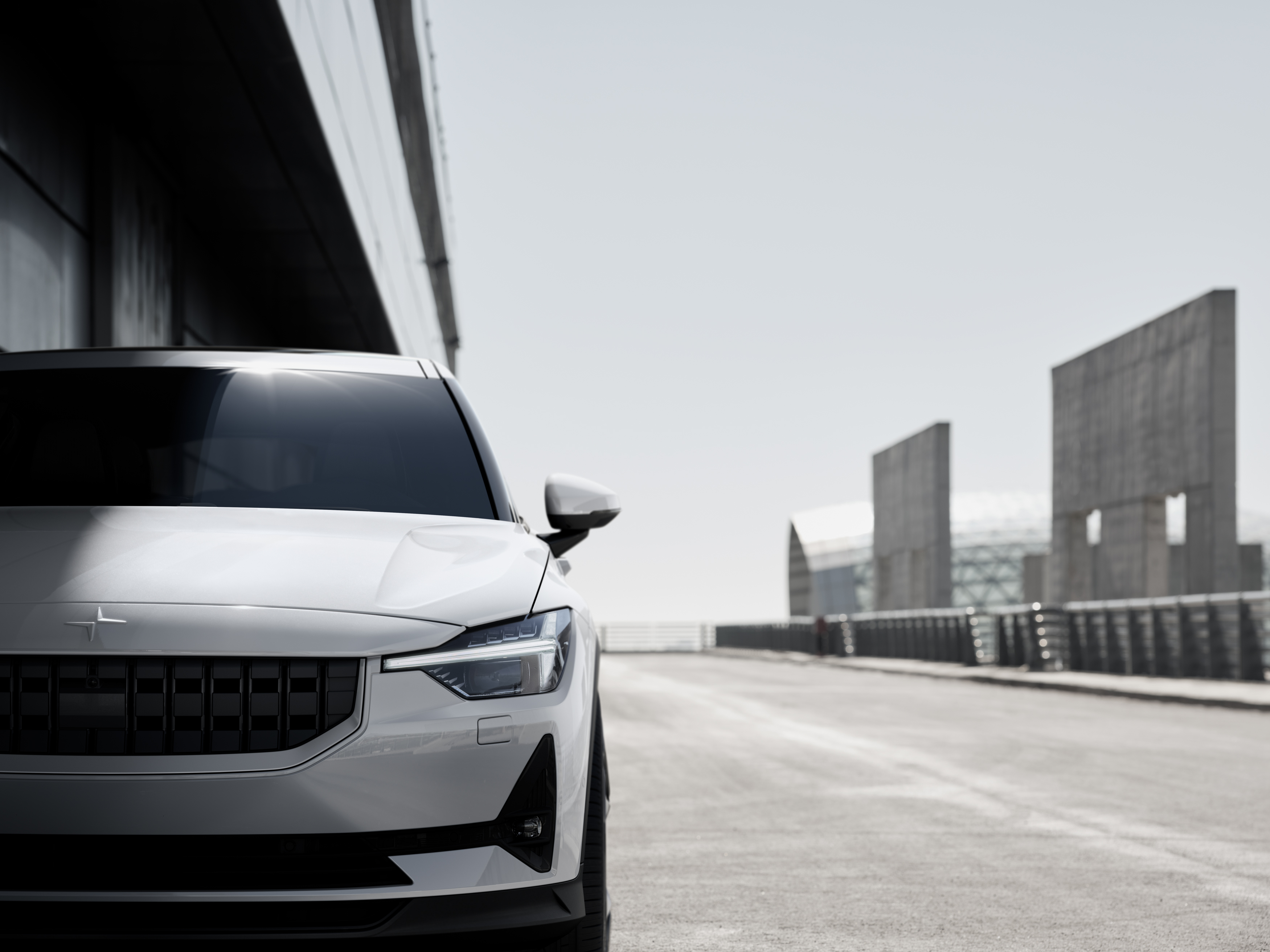
Volvo’s standalone electric performance brand Polestar introduced Wednesday its first all-electric vehicle — a five-door fastback that is gunning for the Tesla Model 3.
In the past few years, every time an electric vehicle — concept, prototype, or production version — has been unveiled, the term “Tesla killer” has been tossed about regardless of whether that car will ever even come to market.
In the case of Polestar 2, it’s unclear if it will be the “Tesla killer.” It’s possible that an entirely new group of customers will be attracted to the vehicle. What is clear: the Polestar 2 was designed to compete with the Tesla Model 3 in the U.S., Europe and China.
You can watch the reveal on Polestar’s YouTube channel.
The specs
The Polestar 2 meant to be a performance electric vehicle. It’s equipped with two electric motors and a 78 kilowatt-hour battery pack that has an estimated EPA range of about 275 miles.
The Polestar 2’s all-wheel drive electric powertrain produces 300 kW ( an equivalent of 408 horsepower) and 487 lb-ft of torque. This is above the rear-wheel (and currently cheapest) version of the Model 3. It’s just a skoosh under the dual-motor performance version of the Model 3, which has an output of 450 horsepower and 471 lb-ft of torque.
The Polestar 2 accelerates from 0 to 100km (about 62 mph) in less than 5 seconds — again a stat that puts it right above the mid-range Model 3 and below the performance version.
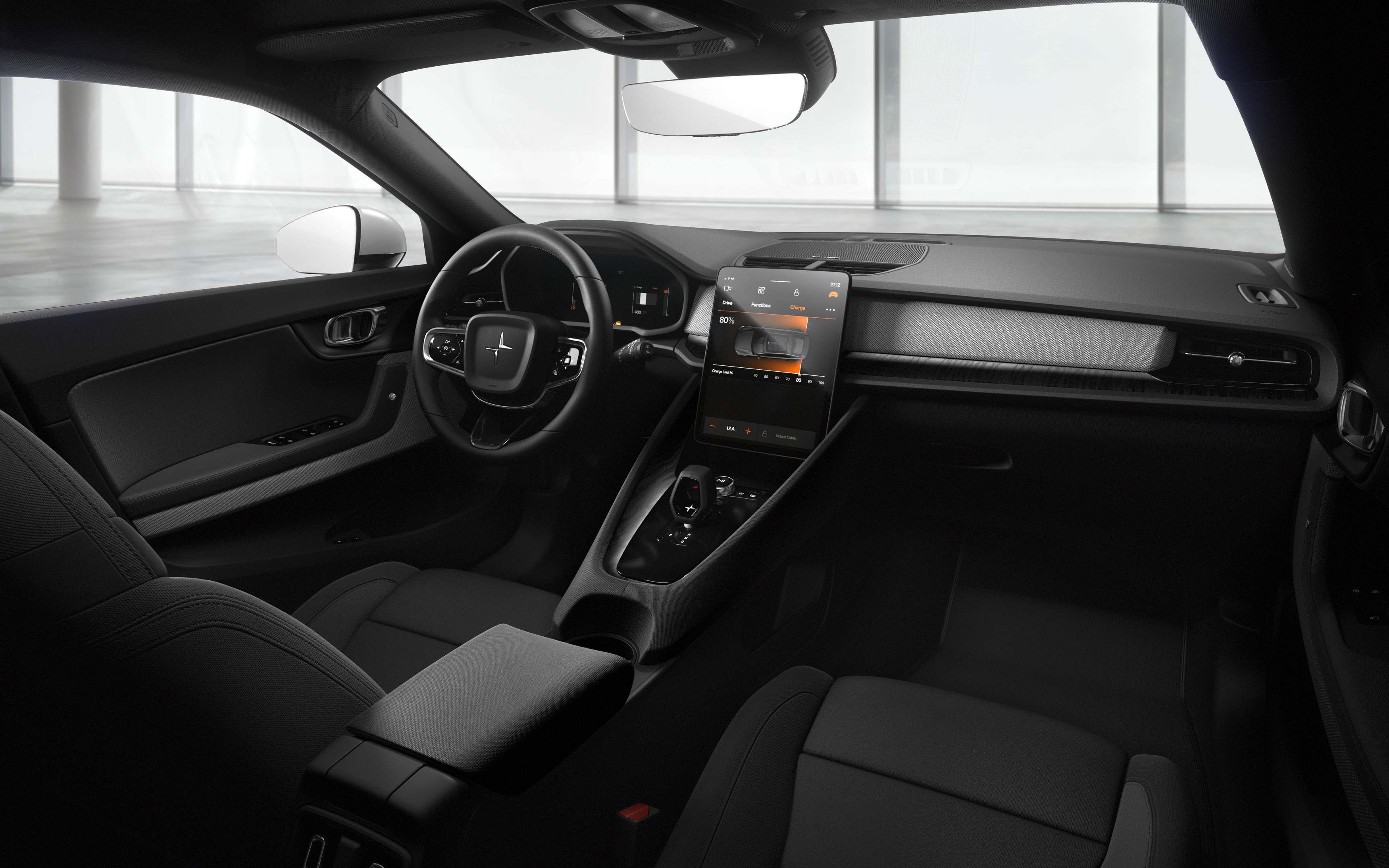
Android inside
In 2017, Volvo announced plans to incorporate a version of its Android operating system into its car infotainment systems. A year later, the company said it would embed voice-controlled Google Assistant, Google Play Store, Google Maps, and other Google services into its next-generation Sensus infotainment system.
Polestar has followed Volvo. The Polestar 2’s infotainment system will be powered by Android OS and as a result, bring embedded Google services such as Google Assistant, Google Maps, and the Google Play Store into the car.
This shouldn’t be confused with Android Auto, which is a secondary interface that lays on top of an operating system. Android OS is modeled after its open-source mobile operating system that runs on Linux. But instead of running smartphones and tablets, Google modified it so it could be used in cars.
The Polestar 2 will also have so-called “Phone-As-Key technology,” which basically means customers will have the ability to unlock their car remotely using their smartphones. This capability opens the door — literally and figuratively — for owners to rent their vehicle out via car sharing or use a delivery service to drop off items in the vehicle.
The feature also allows Polestar 2 to sense the driver upon approach.
Market plans
The base price of Polestar 2 is 39,900 euros ($45,389), the company says. However, for the first year of production the pricier “launch edition” will only be available at 59,900, or about $68,000. (The prices are listed before any federal or state incentives might be applied).
Production of the Polestar 2 will begin in early 2020 at its Chengdu, China factory. The company is initially targeting sales in China, the U.S., Canada and a handful of European countries that include Belgium, Germany, the Netherlands, Norway, Sweden and the UK.
Polestar, like its potential rival Tesla, is also ditching the dealership. Polestar will only sell its vehicles online and will offer customers subscriptions to the vehicle. Subscription pricing will be revealed at a later date, Polestar said.
The automaker is also opening “Polestar Spaces,” a showroom where customers can interact with the product and schedule test drives. These spaces will be standalone facilities and not within existing Volvo retailer showrooms.
Polestar was once a high-performance brand under Volvo Cars. In 2017, the company was recast as an electric performance brand aimed at producing exciting and fun-to-drive electric vehicles — a niche that Tesla was the first to fill and has dominated ever since. Polestar is a jointly owned by Volvo Car Group and Zhejiang Geely Holding of China. Volvo was acquired by Geely in 2010.
The company’s first vehicle, the Polestar 1, was unveiled in September. The Polestar 1 is not a pure electric vehicle; it’s a plug-in hybrid with two electrical motors powered by three 34 kilowatt-hour battery packs and a turbo and supercharged gas inline 4 up front.
Polestar said Wednesday that its next vehicle, the Polestar 3, will be an all-electric “performance SUV.” The company didn’t provide any additional details about the Polestar 3.
from Android – TechCrunch https://ift.tt/2H5zQsX
via IFTTT


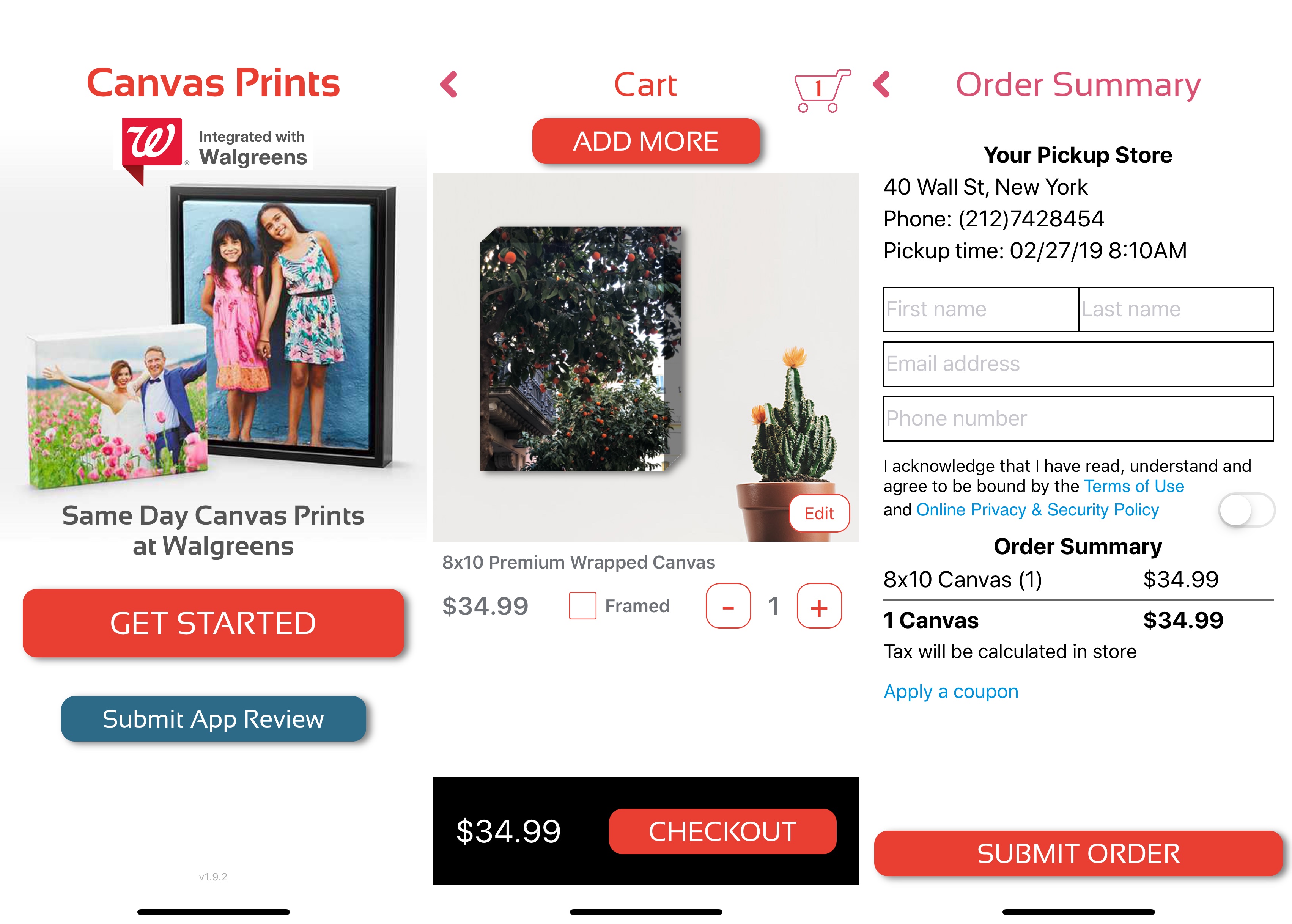


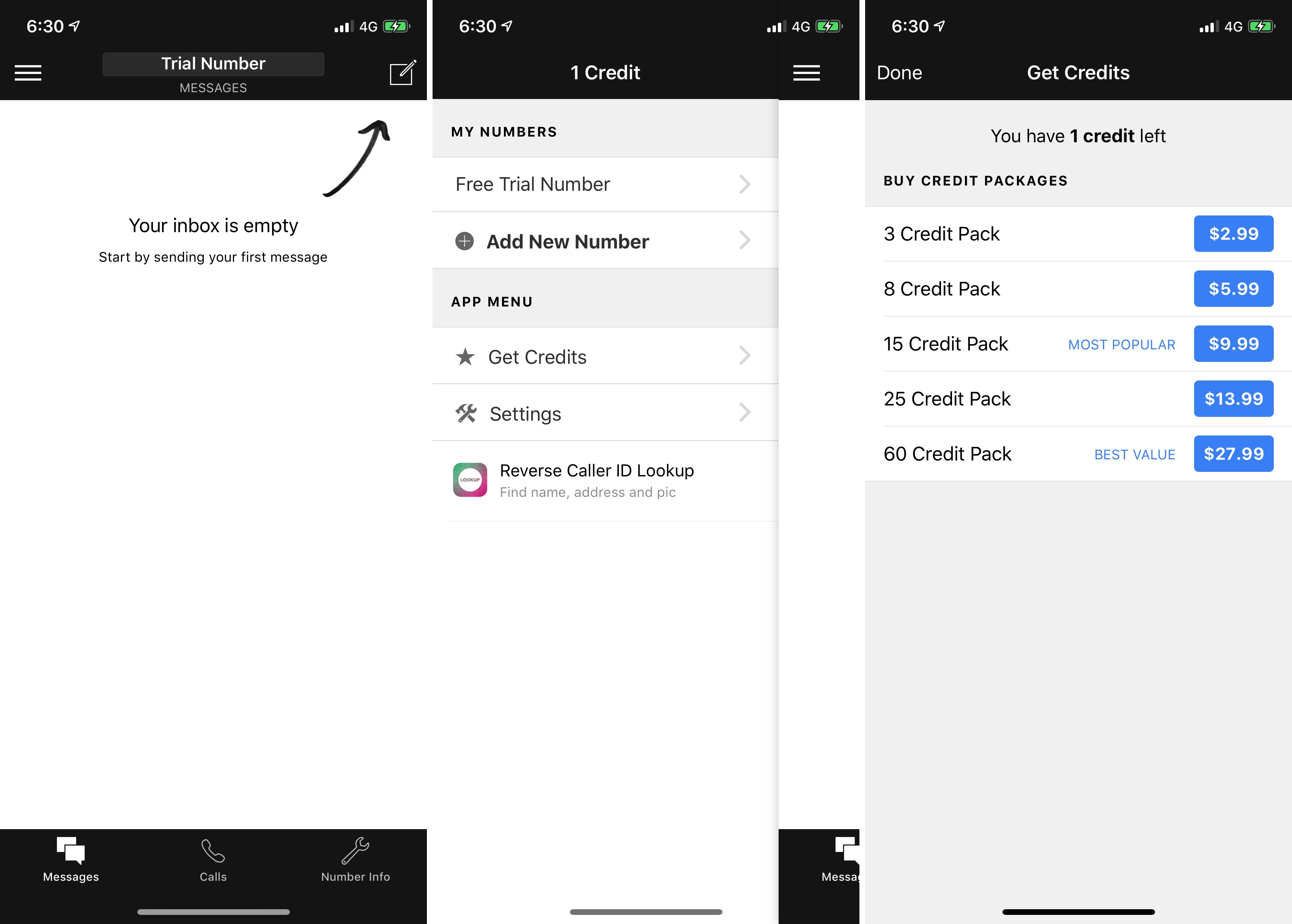
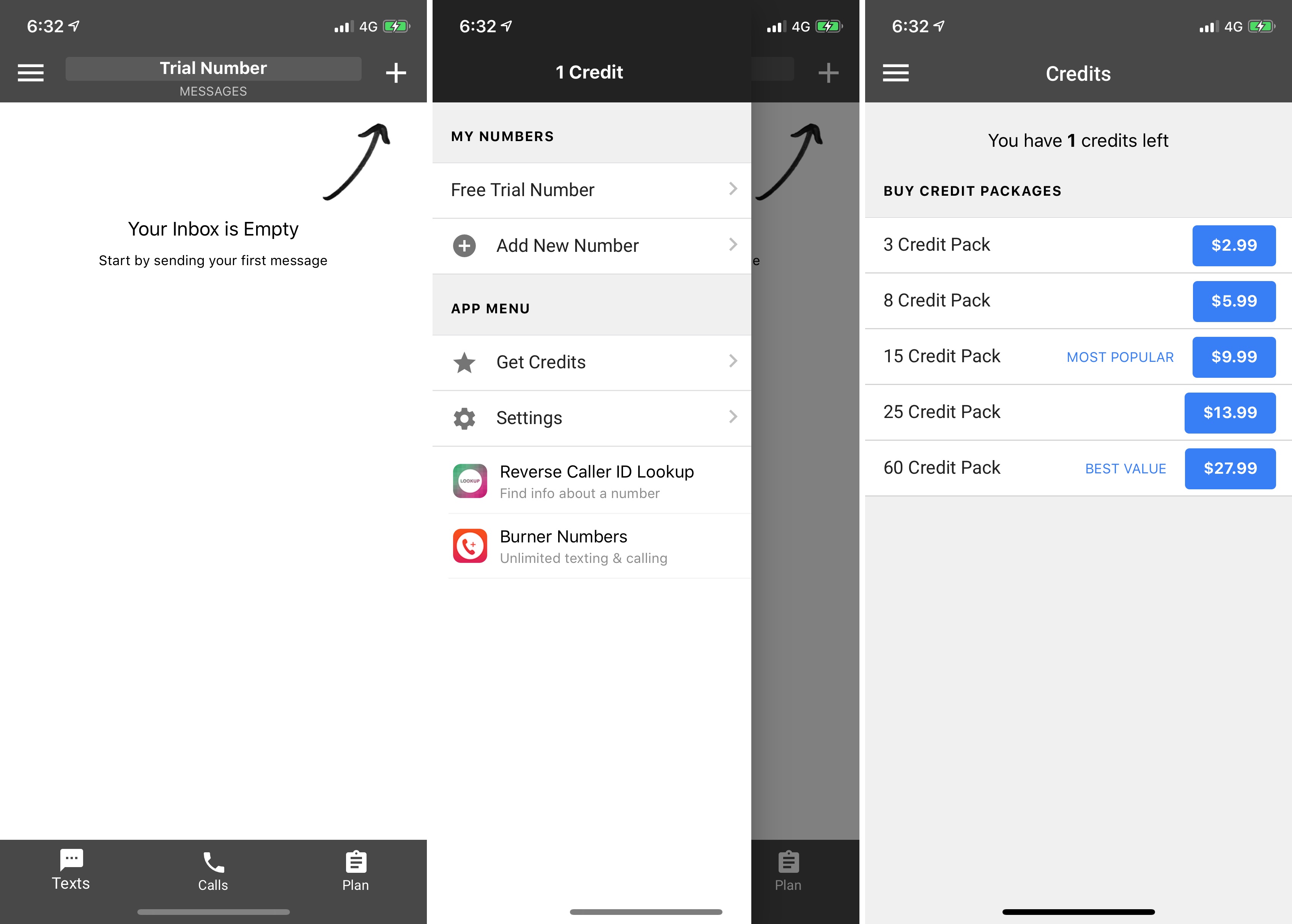



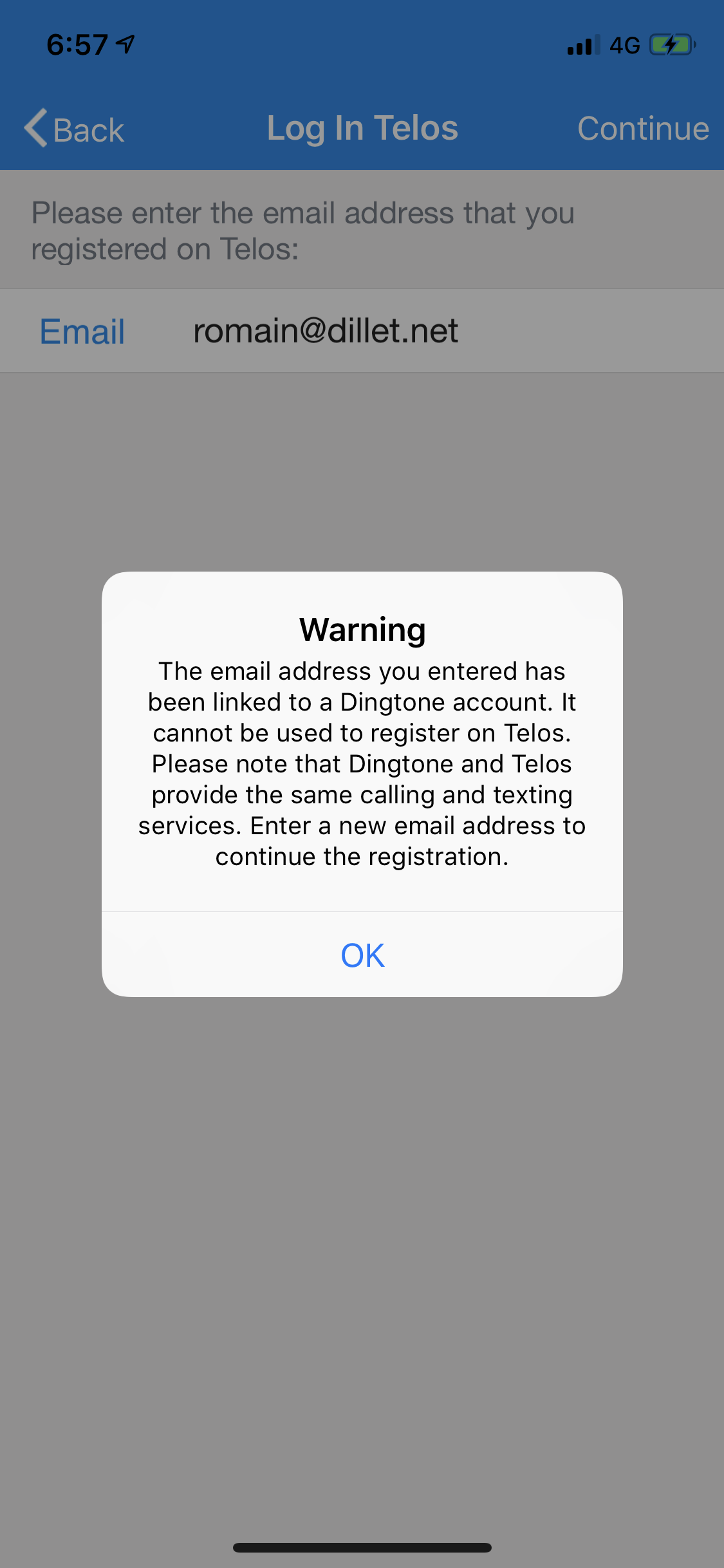
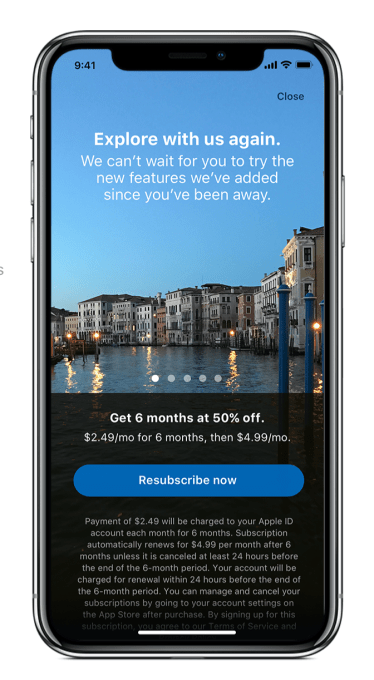 And developers are in control of when an offer displays to a customer, in which territories, as well as how many offers a customer can redeem.
And developers are in control of when an offer displays to a customer, in which territories, as well as how many offers a customer can redeem.