With the release of watchOS 7, Apple at last turned the Apple Watch into the GPS-based kid tracker parents have wanted, albeit at a price point that requires careful consideration. As someone in the target demographic for such a device — a parent of a “tween” who’s allowed to freely roam the neighborhood (but not without some sort of communication device) — I put the new Family Setup system for the Apple Watch through its paces over the past couple of months.
The result? To be frank, I’m conflicted as to whether I’d recommend the Apple Watch to a fellow parent, as opposed to just suggesting that it’s time to get the child a phone.
This has to do, in part, with the advantages offered by a dedicated family tracking solution — like Life360, for example — as well as how a child may respond to the Apple Watch itself, and the quirks of using a solution that wasn’t initially designed with the needs of family tracking in mind.
As a parent of a busy and active tween (nearly 11), I can see the initial appeal of an Apple Watch as a family tracker. It has everything you need for that purpose: GPS tracking, the ability to call and text, alerts, and access to emergency assistance. It’s easy to keep up with, theoretically, and it’s not as pricey as a new iPhone. (The new Apple Watch SE cellular models start at $329. The feature also works on older Apple Watch Series 4 or later models with cellular. Adding on the Apple Watch to your phone plan is usually around $10 per month more.)
I think the Apple Watch as a kid tracker mainly appeals to a specific type of parent: one who’s worried about the dangers of giving a younger child a phone and thereby giving them access to the world of addictive apps and the wider internet. I understand that concern, but I personally disagree with the idea that you should wait until a child is “older,” then hand them a phone and say “ok, good luck with that!” They need a transition period and the “tween” age range is an ideal time frame to get started.
The reality is that smartphones and technology are unavoidable. As a parent, I believe it’s my job to introduce these things in small measures — with parental controls and screen time limits, for example. And then I need to monitor their usage. I may make mistakes and so will my daughter, but we both need these extra years to figure out how to balance parenting and the use of digital tools. With a phone, I know I will have to have the hard conversations about the problems we run into. I understand, too, why parents want to put that off, and just buy a watch instead.

Image Credits: TechCrunch
After my experience, I feel the only cases where I’d fully endorse the Apple Watch would be for those tech-free or tech-light families where kids will not be given phones at any point, households where kids’ phone usage is highly restricted (like those with Wi-Fi only phones), or those where kids don’t get phones until their later teenage years. I am not here to convince them of my alternative, perhaps more progressive view on when to give a kid a phone. The Apple Watch may make sense for these families and that’s their prerogative.
However, a number of people may be wondering if the Apple Watch can be a temporary solution for perhaps a year or two before they buy the child a smartphone. To them, I have to say this feels like an expensive way to delay the inevitable, unavoidable task of having to parent your child through the digital age.
Given my position on the matter, my one big caveat to this review is that my daughter does, in fact, have a smartphone. Also, let’s be clear: this is not meant to be a thorough review of the Apple Watch itself, or a detailed report of its various “tech specs”. It’s a subjective report as to how things went for us that, hopefully, you can learn from.
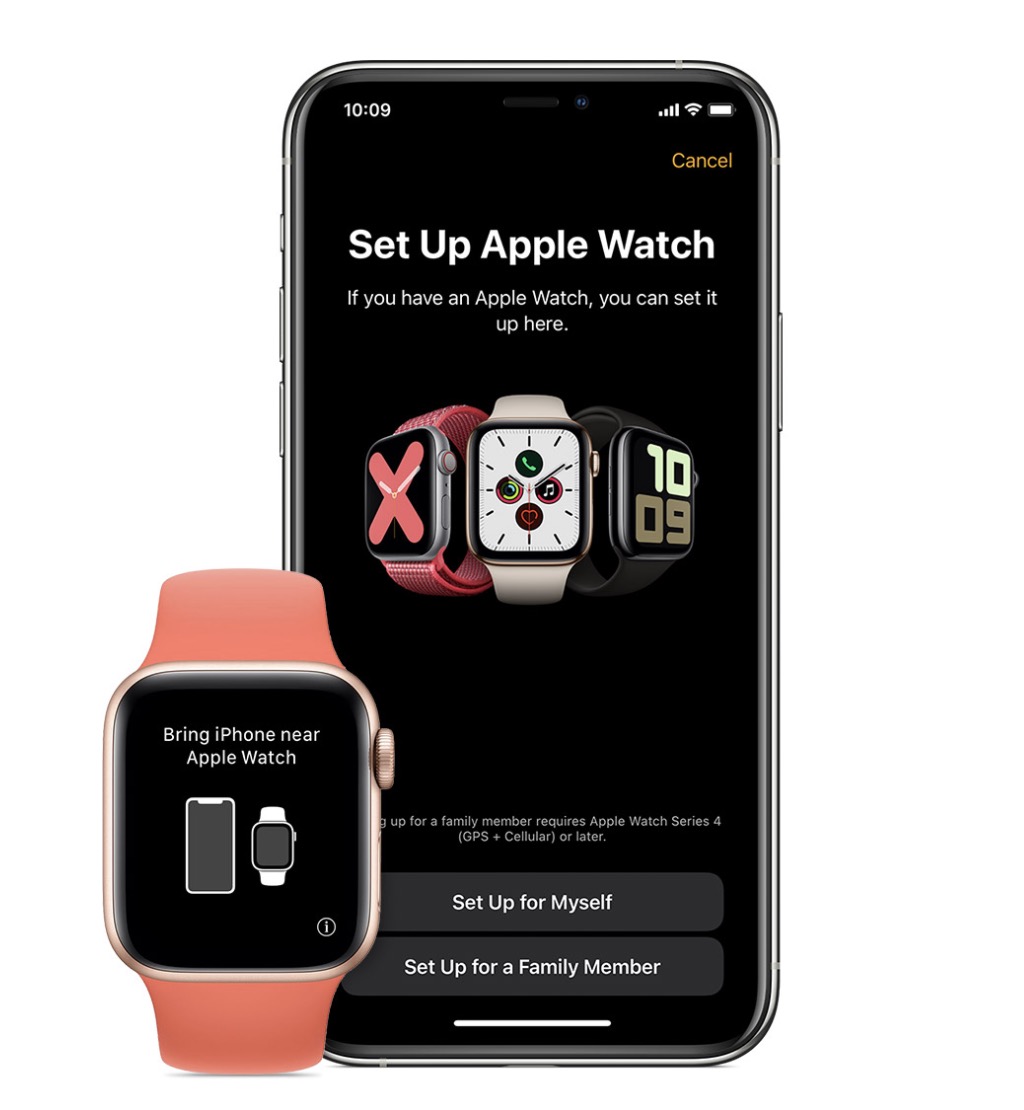
Image Credits: Apple
To begin, the process of configuring the new Apple Watch with Family Setup was easy. “Set Up for a Family Member” is one of two setup options to tap on as you get started. Apple offers a simple user interface that walks you through pairing the Watch with your phone and all the choices that have to be made, like enabling cellular, turning on “Ask to Buy” for app purchases, enabling Schooltime and Activity features, and more.
What was harder was actually using the Apple Watch as intended after it was configured. I found it far easier to launch an iPhone app (like Life360, which we use) where everything you need is in one place. That turned out not to be true for Apple Watch Family Setup system.
For the purpose of testing the Apple Watch with Family Setup, my daughter would leave her iPhone behind when she went out biking or when meeting up with friends for outdoor activities.
As a child who worked her way up to an iPhone over a couple of years, I have to admit I was surprised at how irresponsible she was with the watch in the early weeks.
She didn’t at all respect at the multi-hundred dollar device it was, at first, but rather treated it like her junk jewelry or her wrist-worn scrunchies. The Apple Watch was tossed on a dresser, a bathroom counter, a kitchen table, on a beanbag chair, and so on.
Thankfully, the “Find My” app can locate the Apple Watch, if it has battery and a signal. But I’m not going to lie — there were some scary moments where a dead watch was later found on the back of a toilet (!!), on the top of the piano, and once, abandoned at a friend’s house.
And this, from a child who always knows where her iPhone is!
The problem is that her iPhone is something she learned to be responsible for after years of practice. This fooled me into thinking she actually was responsible for expensive devices. For two years, we painfully went through a few low-end Android phones while she got the hang of keeping up with and caring for such a device. Despite wrapping those starter phones in protective cases, we still lost one to a screen-destroying crash on a tile floor and another to being run over by a car. (How it flew out of a pocket and into the middle of the road, I’ll never understand!)
But, eventually, she did earn access to a hand-me down iPhone. And after initially only being allowed to use it in the house on Wi-Fi, that phone now goes outdoors and has its own phone number. And she has been careful with it in the months since. (Ahem, knocks on wood.)
The Apple Watch, however, held no such elevated status for her. It was not an earned privilege. It was not fun. It was not filled with favorite apps and games. It was, instead, thrust upon her.
While the iPhone is used often for enjoyable and addictive activities like Roblox, TikTok, Disney+, and Netflix, the Apple Watch was boring by comparison. Sure, there are a few things you can do on the device — it has an App Store! You can make a Memoji! You can customize different watch faces! But unless this is your child’s first-ever access to technology, these features may have limited appeal.
“Do you want to download this game? This looks fun,” I suggested. pointing to a coloring game, as we looked at her Watch together one night.
“No thanks,” she replied.
“Why not?”
“I just think don’t think it would be good on the little screen.”
“Maybe a different game?”
“Nah.”
And that was that. I could not convince her to give a single Apple Watch app a try in the days that followed.
She didn’t even want to stream music on the Apple Watch — she has Alexa for that, she pointed out. She didn’t want to play a game on the watch — she has Roblox on the bigger screen of her hand-me down laptop. She also has a handheld Nintendo Switch.

Image Credits: TechCrunch
Initially, she picked an Apple Watch face that matched her current “aesthetic” — simple and neutral — and that was the extent of her interest in personalizing the device in the first several weeks.
Having already burned herself out on Memoji by borrowing my phone to play with the feature when it launched, there wasn’t as much interest in doing more with the customized avatar creation process, despite my suggestions to try it. (She had already made a Memoji her Profile photo for her contact card on iPhone.)
However, I later showed her the Memoji Watch Face option after I set it up, and asked her if she liked it. She responded “YESSSS. I love it,” and snatched the watch from my hand to play some more.
Demo’ing features is important, it seems.
But largely, the Apple Watch was only strapped on only at my request as she walked out the door.
Soon, this became a routine.
“Can I go outside and play?”
“Yes. Wear the watch!,” I’d reply.
“I knowwww.”
It took over a month to get to the point that she would remember the watch on her own.
I have to admit that I didn’t fully demo the Apple Watch to her or explain how to use it in detail, beyond a few basics in those beginning weeks. While I could have made her an expert, I suppose, I think it’s important to realize that many parents are less tech-savvy than their kids. The children are often left to fend for themselves when it comes to devices, and this particular kid has had several devices. For that reason, I was curious how a fairly tech literate child who has moved from iPad to Android to now iPhone, and who hops from Windows to Mac to Chromebook, would now adapt to an Apple Watch.
As it turned out, she found it a little confusing.
“What do you think about the Watch?” I asked one evening, feeling her out for an opinion.
“It’s fun…but sometimes I don’t really understand it,” she replied.
“What don’t you understand?”
“I don’t know. Just…almost everything,” she said, dramatically, as tweens tend to do. “Like, sometimes I don’t know how to turn up and down the volume.”
Upon prodding, I realize she meant this: she was confused about how to adjust the alert volume for messages and notifications, as well as how to change the Watch from phone calls to a vibration or to silence calls altogether with Do Not Disturb. (It was her only real complaint, but annoying enough to be “almost everything,” I guess!)
I’ll translate now from kid language what I learned here.
First, given that the “Do Not Disturb” option is accessible from a swipe gesture, it’s clear my daughter hadn’t fully explored the watch’s user interface. It didn’t occur to her that the swipe gestures of the iPhone would have their own Apple Watch counterparts. (And also, why would you swipe up from the bottom of the screen for the Control Center when that doesn’t work on the iPhone anymore? On iPhone, you now swipe down from the top-right to get to Control Center functions.)
And she definitely hadn’t discovered the tiny “Settings” app (the gear icon) on the Apple Watch’s Home Screen to make further changes.
Instead, her expectation was that you should be able to use either a button on the side for managing volume — you know, like on a phone — or maybe the digital crown, since that’s available here. But these physical features of the device — confusingly — took her to that “unimportant stuff” like the Home Screen and an app switcher, when in actuality, it was calls, notifications, and alerts that were the app’s main function, in her opinion.
And why do you need to zoom into the Home Screen with a turn of the digital crown? She wasn’t even using the apps at this point. There weren’t that many on the screen.
Curious, since she didn’t care for the current lineup of apps, I asked for feedback.
“What kind of apps do you want?,” I asked.
“Roblox and TikTok.”
“Roblox?!,” I said, laughing. “How would that even work?”
As it turned out, she didn’t want to play Roblox on her watch. She wanted to respond to her incoming messages and participate in her group chats from her watch.
Oh. That’s actually a reasonable idea. The Apple Watch is, after all, a messaging device.
And since many kids her age don’t have a phone or the ability to use a messaging app like Snapchat or Instagram, they trade Roblox usernames and friend each other in the game as way to work around this restriction. They then message each other to arrange virtual playdates or even real-life ones if they live nearby.
But the iOS version of the Roblox mobile app doesn’t have an Apple Watch counterpart.
“And TikTok?” I also found this hilarious.
But the fact that Apple Watch is not exactly an ideal video player is lost on her. It’s a device with a screen, connected to the internet. So why isn’t that enough, she wondered?
“You could look through popular TikToks,” she suggested. “You wouldn’t need to make an account or anything,” she clarified, as these details were would fix the only problems she saw with her suggestion.
Even if the technology was there, a TikTok experience on the small screen would never be a great one. But this goes to show how much interest in technology is directly tied to what apps and games are available, compared with the technology platform itself.
Other built-in features had even less appeal than the app lineup.
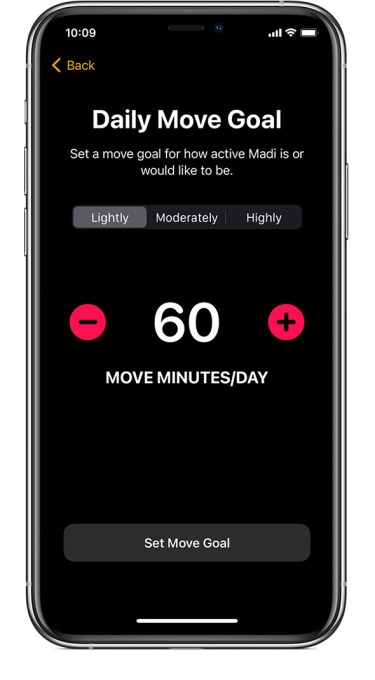
Image Credits: Apple
Though I had set up some basic Activity features during the setup process, like a “Move Goal,” she had no idea what any of that was. So I showed her the “rings” and how they worked, and she thought it was kind of neat that the Apple Watch could track her standing. However, there was no genuine interest or excitement in being able quantify her daily movement — at least, not until one day many weeks later when were hiking and she heard my watch ding as my rings closed and wanted to do the same on hers. She became interested in recording her steps for that hike, but the interest wasn’t sustained afterwards.
Apple said it built in the Activity features so kids could track their move goal and exercise progress. But I would guess many kids won’t care about this, even if they’re active. After all, kids play — they don’t think “how much did I play?” Did I move enough today? And nor should they, really.
As a parent, I can see her data in the Health app on my iPhone, which is the device I use to manage her Apple Watch. It’s interesting, perhaps, to see things like her steps walked or flights climbed. But it’s not entirely useful, as her Apple Watch is not continually worn throughout the day. (She finds the bands uncomfortable — we tried Sport Band and Sport Loop and she still fiddles with them constantly, trying to readjust them for comfort.)
In addition, if I did want to change her Activity goals later on for some reason, I’d have to do from her Watch directly.
Of course, a parent doesn’t buy a child an Apple Watch to track their exercise. It’s for the location tracking features. That is the only real reason a parent would consider this device for a younger child.
On that front, I did like that the watch was a GPS tracker that was looped into our household Apple ecosystem as its own device with its own phone number. I liked that I could ping the Watch with “Find My” when it’s lost — and it was lost a lot, as I noted. I liked that I could manage the Watch from my iPhone, since it’s very difficult to reacquire a device to make changes, once it’s handed over to someone else.
I also liked the Apple Watch was always available for use. This may have been one of its biggest perks, in fact. Unlike my daughter’s iPhone, which is almost constantly at 10-20% battery (or much less), the watch was consistently charged and ready when it was time for outdoor play.
I liked that it was easier for her to answer a call on the Apple Watch compared with digging her phone out of her bike basket or bag. I liked that she didn’t have to worry about constantly holding onto her phone while out and about.
I also appreciated that I could create geofenced alerts — like when she reached the park or a friend’s house, for example, or when she left. But I didn’t like that the ability to do so is buried in the “Find My” app. (You tap on the child’s name in the “People” tab. Tap “Add” under “Notifications.” Tap “Notify Me.” Tap “New Location.” Do a search for an address or venue. Tap “Done.”)
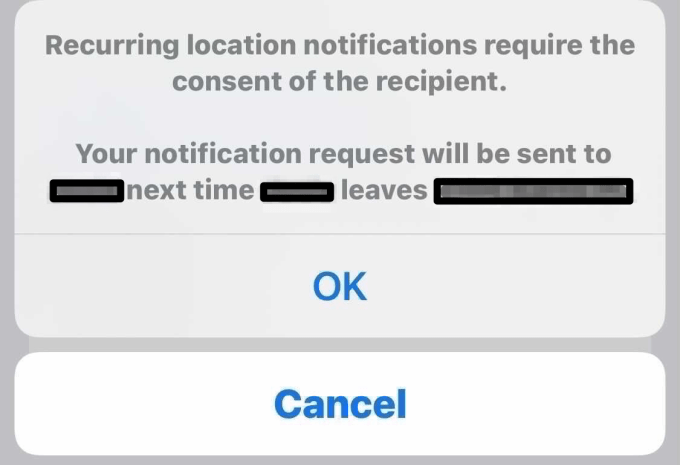
Image Credits: TechCrunch
I also didn’t like that when I created a recurring geofence, my daughter would be notified. Yes, privacy. I know! But who’s in charge here? My daughter is a child, not a teen. She knows the Apple Watch is a GPS tracker — we had that conversation. She knows it allows me to see where she is. She’s young and for now, she doesn’t feel like this a privacy violation. We’ll have that discussion later, I’m sure. But at the present, she likes the feel of this electronic tether to home as she experiments with expanding the boundaries of her world.
When I tweak and update recurring alerts for geofenced locations, such alerts can be confusing or even concerning. I appreciate that Apple is being transparent and trying to give kids the ability to understand they’re being tracked — but I’d also argue that most parents who suddenly gift an expensive watch to their child will explain why they’re doing so. This is a tool, not a toy.
Also, the interface for configuring geofences is cumbersome. By comparison, the family tracking app Life360 which we normally use has a screen where you simply tap add, search to find the location, and then you’re done. One tap on a bell icon next to the location turns on or off its alerts. (You can get all granular about it: recurring, one time, arrives, leaves, etc. — but you don’t have to. Just tap and be alerted. It’s more straightforward.)
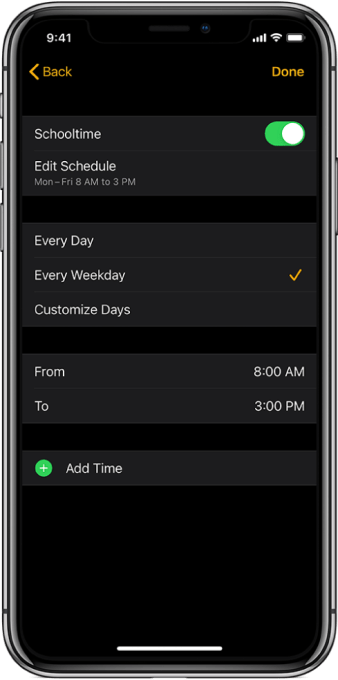
Image Credits: Apple
One feature I did like on the Apple Watch, but sadly couldn’t really use, was its Schooltime mode — a sort of remotely-enabled, scheduled version of Do Not Disturb. This feature blocks apps and complications and turns on the Do Not Disturb setting for the kids, while letting emergency calls and notifications break through. (Make sure to set up Shared Contacts, so you can manage that aspect.)
Currently, we have no use for Schooltime, thanks to this pandemic. My daughter is attending school remotely this year. I could imagine how this may be helpful one day when she returns to class.
But I also worry that if I sent her to class with the Apple Watch, other kids will judge her for her expensive device. I worry that teachers (who don’t know about Schooltime), will judge me for having her wear it. I worry kids will covet it and ask to try it on. I worry a kid running off with it, causing additional disciplinary headaches for teachers. I worry it will get smashed on the playground or during PE, or somehow fall off because she meddled with the band for the umpteenth time. I worry she’ll take it off because “the strap is so annoying” (as I was told), then leave it in her desk.
I don’t worry as much about the iPhone at school, because it stays in her backpack the whole time due to school policy. It doesn’t sit on her arm as a constant temptation, “Schooltime” mode or otherwise.
The Apple Watch Family Setup is also not a solution that adapts as the child ages to the expanding needs of teen monitoring, compared with other family tracking solutions.
To continue the Life360 comparison, the app today offers features for teen drivers and its new privacy-sensitive location “bubbles” for teens now give them more autonomy. Apple’s family tracking solution, meanwhile, becomes more limited as the child ages up.
For instance, Schooltime doesn’t work on an iPhone. Once the child upgrades to an iPhone, you are meant to use parental controls and Screen Time features to manage what apps are allowed and when she can use her device. It seems a good transitional step to the phone would be a way to maintain Schooltime mode on the child’s next device, too.
Instead, by buying into Apple Watch for its Family Setup features, what you’ll soon end up with is a child who now owns both an Apple Watch and a smartphone. (Sure, you could regift it or take it back, I suppose…I certainly do wish you luck if you try that!)
Beyond the overboard embrace of consumerism that is buying an Apple Watch for a child, the biggest complaint I had was that there were three different apps for me to use to manage and view data associated with my daughter’s Apple Watch. I could view her tracked activity was tracked in my Health app. Location-tracking and geofence configuration was in the Find My app. And remotely configuring the Apple Watch itself, including Schooltime, was found in my Watch mobile app.
I understand that Apple built the Watch to be a personal device designed for use with one person and it had to stretch to turn it into a family tracking system. But what Apple is doing here is really just pairing the child’s watch with the parent’s iPhone and then tacking on extra features, like Schooltime. It hasn’t approached this as a whole new system designed from the ground-up for families or for their expanding needs as the child grows.
As a result, the whole system feels underdeveloped compared with existing family tracking solutions. And given the numerous features to configure, adjust, and monitor, Family Setup deserves its own app or at the very least, its own tab in a parent’s Watch app to simplify its use.
At the end of the day, if you are letting your child out in the world — beyond school and supervised playdates — the Apple Watch is a solution, but it may not be the best solution for your needs. If you have specific reasons why your child will not get their own phone now or anytime soon, the Apple Watch may certainly work. But if you don’t have those reasons, it may be time to try a smartphone.
Both Apple and Google now offer robust parental control solutions for their smartphone platforms that can mitigate many parents’ concerns over content and app addiction. And considering the cost of a new Apple Watch, the savings just aren’t there — especially when considering entry-level Android phones or other hand-me-down phones as the alternative.
[Apple provided a loaner device for the purposes of this review. My daughter was cited and quoted with permission but asked for her name to not be used.]

from Apple – TechCrunch https://ift.tt/2KUqJiJ